Prehistoric Cornwall Canals (Dykes)
GE Map of Prehistoric Cornwall Canals (Dykes)
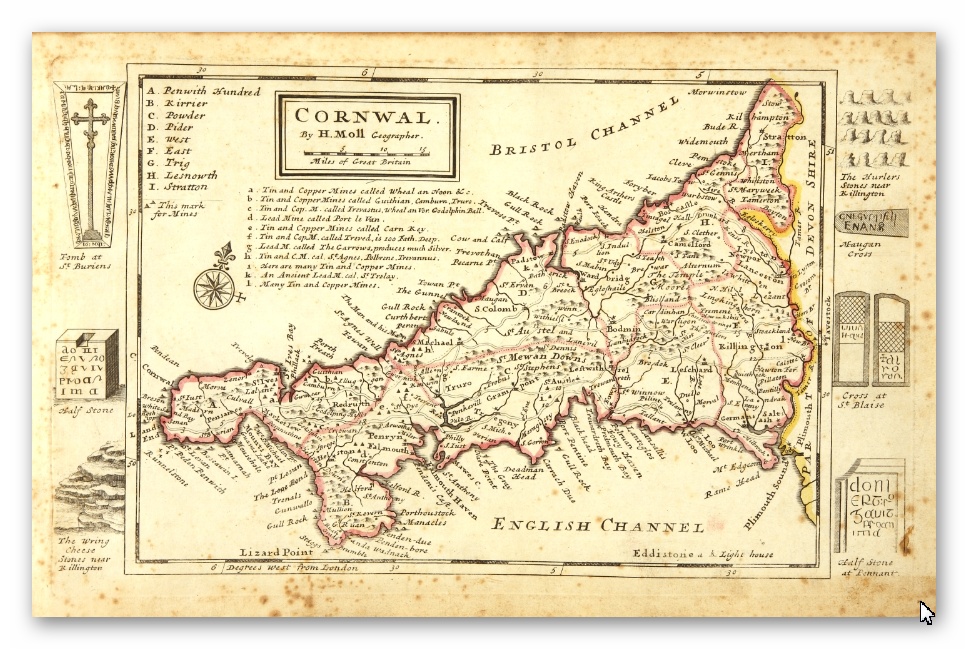
Old Map
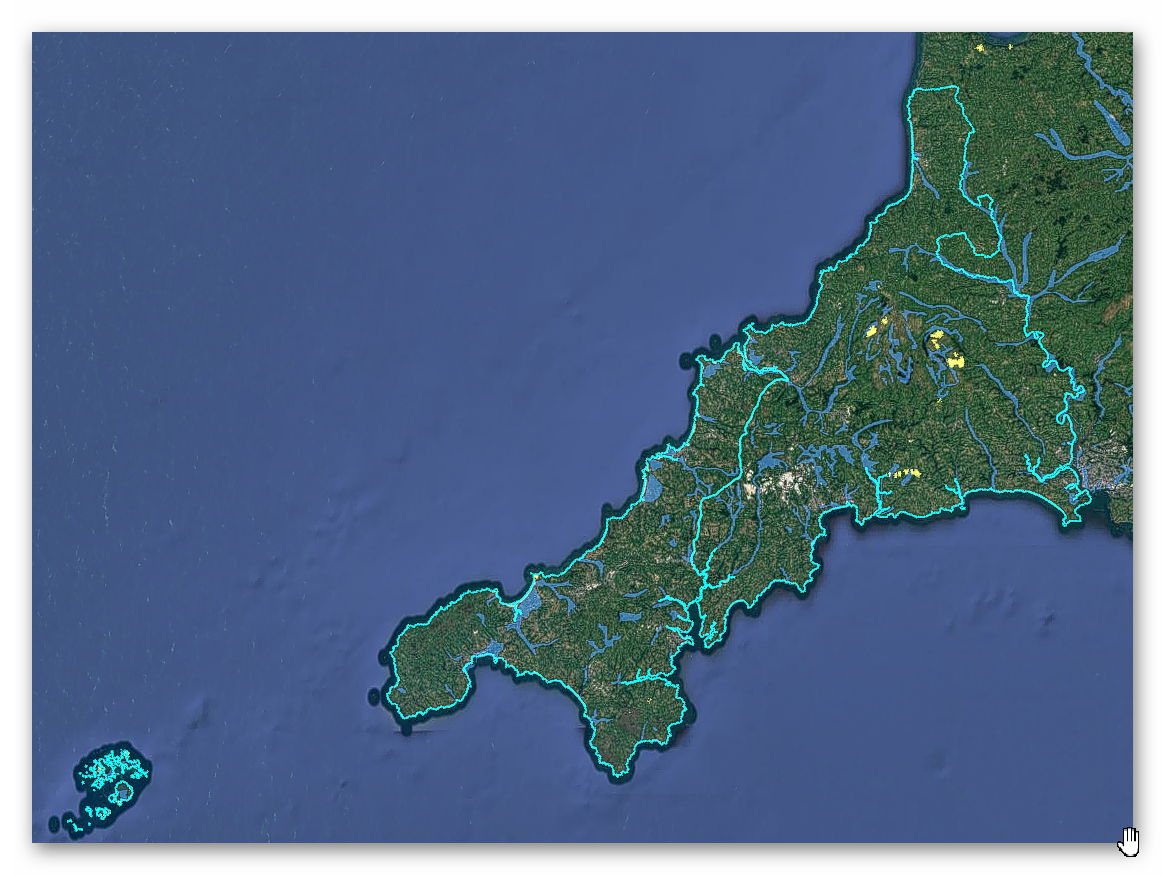
Geological Landscape
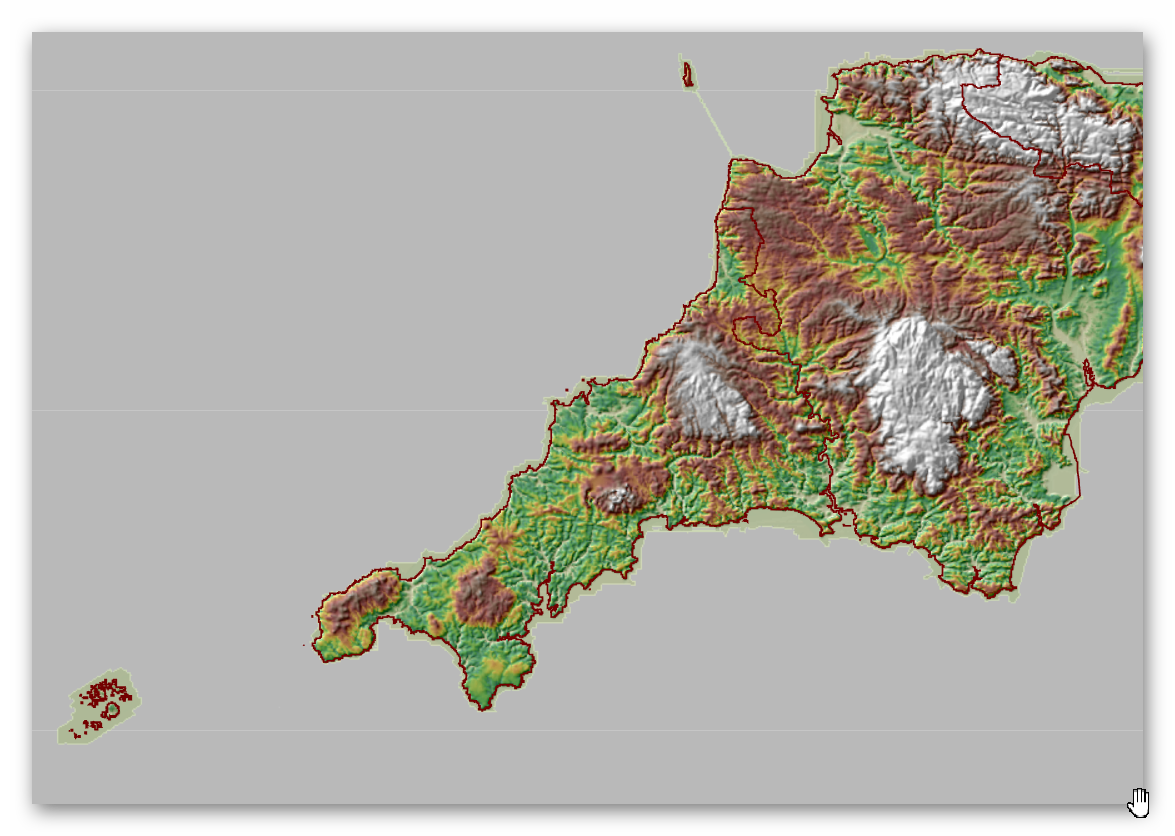
Landscape/Terrain
Database of DYKES (Linear Earthworks) in Cornwall
(Click the ‘HE Entry Ref: Number’ (if blue) for more details and Maps)
| Name | HE Entry Ref: | NGF | Length (m) | Overall Width (m) | Ditch Width (m) | Bank Width (m) |
| Earthwork 100yds (90m) ESE of Tregidden | 1004335 | SW 75573 22941 | ||||
| Part of a medieval boundary dyke 220m east of Golitha House | 1004364 | SX 22671 68380 | ||||
| Linear boundary called the Giant's Hedge | 1006681 | SX 17149 57451 | ||||
| Linear earthworks, probably 17th century, W of Godrevy | 1007284 | SW 58253 43029 | ||||
| Stannon Stone Circle, prehistoric field system, hut circle settlement, cairns, cist, linear boundaries and medieval building north of Dinnever Hill | 1007764 | SX 12685 79833 | ||||
| Prehistoric embanked platform cairn and linear boundary with superimposed medieval boundary and adjacent clearance cairn on Dinnever Hill | 1007768 | SX 12135 79284 | ||||
| Prehistoric linear boundary, adjacent irregular aggregate field system and hut circles, incorporated cairns and medieval grave on north-west Roughtor | 1008187 | SX 14474 81056 | ||||
| Prehistoric coaxial field system, incorporated and adjacent hut circles, stone setting, linear boundaries and medieval settlement on Fox Tor and Treburland Farm | 1008245 | SX 22958 78720 | ||||
| Prehistoric linear boundary and adjacent round cairn 938m north-west of Wardbrook Farm | 1008845 | SX 24958 73842 | ||||
| Prehistoric linear boundary with adjacent stone hut circle, two round cairns and cairnfield 1.125km north of Wardbrook Farm | 1008897 | SX 25278 74283 | ||||
| Unenclosed hut circle settlement and adjacent Prehistoric linear boundary 800m SSE of Trewortha Farm | 1008958 | SX 24747 74384 | ||||
| Prehistoric linear boundaries, cairn and enclosure 1.225km north-west of Wardbrook Farm | 1008982 | SX 24751 74149 | ||||
| Unenclosed hut circle settlement with adjacent enclosure and linear boundary 1.41km SW of East Castick Farm | 1009805 | SX 25492 75416 | ||||
| Three adjoining Prehistoric linear boundaries on Bearah Tor, 687m SW of Nodmans Bowda Farm | 1010220 | SX 26390 74637 | ||||
| Neolithic long cairn, Prehistoric regular and irregular aggregate field systems, linear boundaries and medieval enclosure 625m W of Blackcoombe Farm | 1010221 | SX 26296 73871 | ||||
| Prehistoric and medieval linear boundary 1.34km south of Eastmoorgate | 1011386 | SX 22081 77603 | ||||
| Prehistoric embanked avenue with incorporated funerary cist 210m WNW of Showery Tor | 1011501 | SX 14728 81380 | ||||
| Prehistoric and medieval linear boundary with associated peat stack platform 475m SSW of Eastmoorgate | 1011509 | SX 22059 78374 | ||||
| Prehistoric linear boundary and adjacent subsidiary boundary 1km west of Tresellern Farm | 1011874 | SX 22645 76808 | ||||
| Linear bowl barrow group on Ligger Point, 250m west of Penhale Mine | 1016990 | SW 75927 58032 | ||||
| Prehistoric linear boundary and field system, medieval enclosure and tin miners' caches 1.06km north-west of Wardbrook Farm | 1015975 | SX 24678 73939 | ||||
| Prehistoric linear boundary on Dropnose Point, Gugh | 1008324 | SV 89322 08103 | ||||
| Three platform cairns and adjacent prehistoric linear boundary on Wingletang Down, 70m west of Crooked Rock | 1009276 | SV 88521 07686 | ||||
| Prehistoric linear boundary 50m ENE of Mount Todden Battery, St Mary's | 1010165 | SV 93042 11575 | ||||
| Prehistoric linear boundary on Puffin Island | 1010175 | SV 88154 13429 | ||||
| Prehistoric linear boundary south east of Horse Rock on Porth Hellick Down, St Mary's | 1013668 | SV 92992 10793 | ||||
| Prehistoric field system and kerbed cairn, with post-medieval kelp pit and linear boundary on southern White Island | 1014789 | SV 92508 17341 | ||||
| Prehistoric linear boundary SSE of The Island, Bryher | 1014991 | SV 88128 14815 | ||||
| Prehistoric linear boundary and Civil War fieldworks on north western Toll's Hill, St Mary's | 1015662 | SV 92664 12154 | ||||
| Prehistoric linear boundaries, house platform and cairn on south western Peninnis Head, St Mary's | 1015669 | SV 90974 09526 | ||||
| Prehistoric linear boundary and cairns south west of The Bar, Bryher | 1016170 | SV 88144 15093 |
Dykes Ditches and Earthworks
Indeed, the modern term “dyke” or “dijk” can be traced back to its Dutch origins. As early as the 12th century, the construction of Dykes in the Netherlands was a well-established practice. One remarkable example of their ingenuity is the Westfriese Omringdijk, stretching an impressive 126 kilometres (78 miles), completed by 1250. This Dyke was formed by connecting existing older ‘dykes’, showcasing the Dutch mastery in managing their aquatic landscape.
The Roman chronicler Tacitus even provides an intriguing historical account of the Batavi, a rebellious people who employed a unique defence strategy during the year AD 70. They punctured the Dykes daringly, deliberately flooding their land to thwart their enemies and secure their retreat. This historical incident highlights the vital role Dykes played in the region’s warfare and water management.
Originally, the word “dijk” encompassed both the trench and the bank, signifying a comprehensive understanding of the Dyke’s dual nature – as both a protective barrier and a channel for water control. This multifaceted concept reflects the profound connection between the Dutch people and their battle against the ever-shifting waters that sought to reclaim their land.
The term “dyke” evolved as time passed, and its usage spread beyond the Dutch borders. Today, it represents not only a symbol of the Netherlands’ engineering prowess but also a universal symbol of human determination in the face of the relentless forces of nature. The legacy of these ancient Dykes lives on, a testament to the resilience and innovation of those who shaped the landscape to withstand the unyielding currents of time.
Upon studying archaeology, whether at university or examining detailed ordinance survey maps, one cannot help but encounter peculiar earthworks scattered across the British hillsides. Astonishingly, these enigmatic features often lack a rational explanation for their presence and purpose. Strangely enough, these features are frequently disregarded in academic circles, brushed aside, or provided with flimsy excuses for their existence. The truth is, these earthworks defy comprehension unless we consider overlooked factors at play.
One curious observation revolves around the term “Dyke,” inherently linked to water. It seems rather peculiar to apply such a word to an earthwork atop a hill unless an ancestral history has imparted its actual function through the ages. Let us consider the celebrated “Offa’s Dyke,” renowned for its massive linear structure, meandering along some of the present boundaries between England and Wales. This impressive feat stands as a testament to the past, seemingly demarcating the realms of the Anglian kingdom of Mercia and the Welsh kingdom of Powys during the 8th century.
However, delving further into the evidence and historical accounts challenges this seemingly straightforward explanation. Roman historian Eutropius, in his work “Historiae Romanae Breviarium”, penned around 369 AD, mentions a grand undertaking by Septimius Severus, the Roman Emperor, from 193 AD to 211 AD. In his pursuit of fortifying the conquered British provinces, Severus constructed a formidable wall stretching 133 miles from coast to coast.
Yet, intriguingly, none of the known Roman defences match this precise length. Hadrian’s Wall, renowned for its defensive prowess, spans a mere 70 miles. Could Eutropius have referred to Offa’s Dyke, which bears remarkable similarity to the Roman practice of initially erecting banks and ditches for defence?
For more information click HERE
Further Reading
For information about British Prehistory, visit www.prehistoric-britain.co.uk for the most extensive archaeology blogs and investigations collection, including modern LiDAR reports. This site also includes extracts and articles from the Robert John Langdon Trilogy about Britain in the Prehistoric period, including titles such as The Stonehenge Enigma, Dawn of the Lost Civilisation and the ultimate proof of Post Glacial Flooding and the landscape we see today.
Robert John Langdon has also created a YouTube web channel with over 100 investigations and video documentaries to support his classic trilogy (Prehistoric Britain). He has also released a collection of strange coincidences that he calls ‘13 Things that Don’t Make Sense in History’ and his recent discovery of a lost Stone Avenue at Avebury in Wiltshire called ‘Silbury Avenue – the Lost Stone Avenue’.
Langdon has also produced a series of ‘shorts’, which are extracts from his main body of books:
For active discussions on the findings of the TRILOGY and recent LiDAR investigations that are published on our WEBSITE, you can join our and leave a message or join the debate on our Facebook Group.
